“The most effective medicine is the natural healing power that resides within each of us.”
Hippocrates of Kos
Dear Patients and Parents!
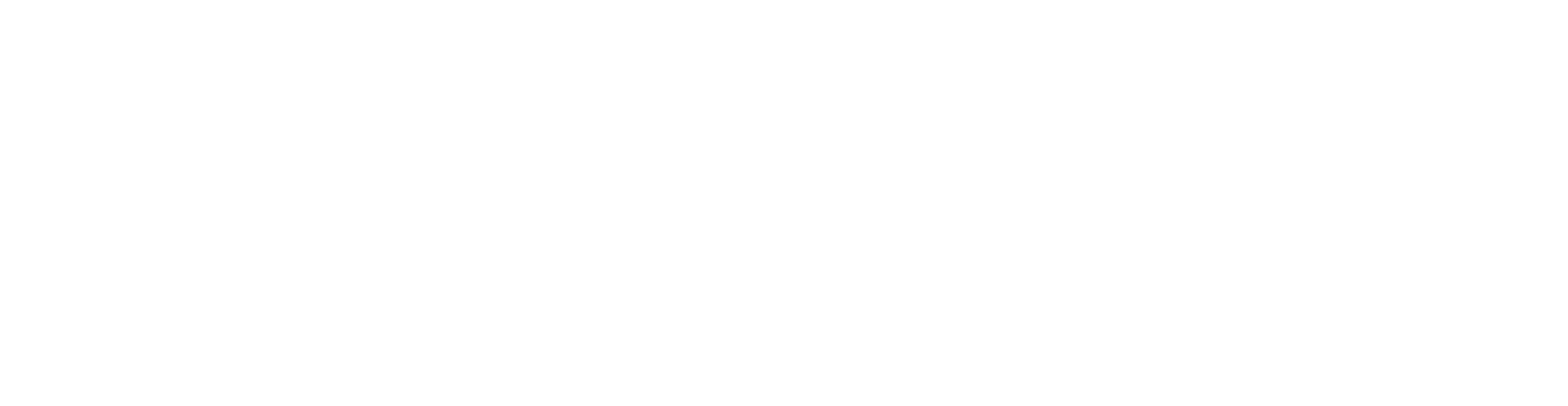
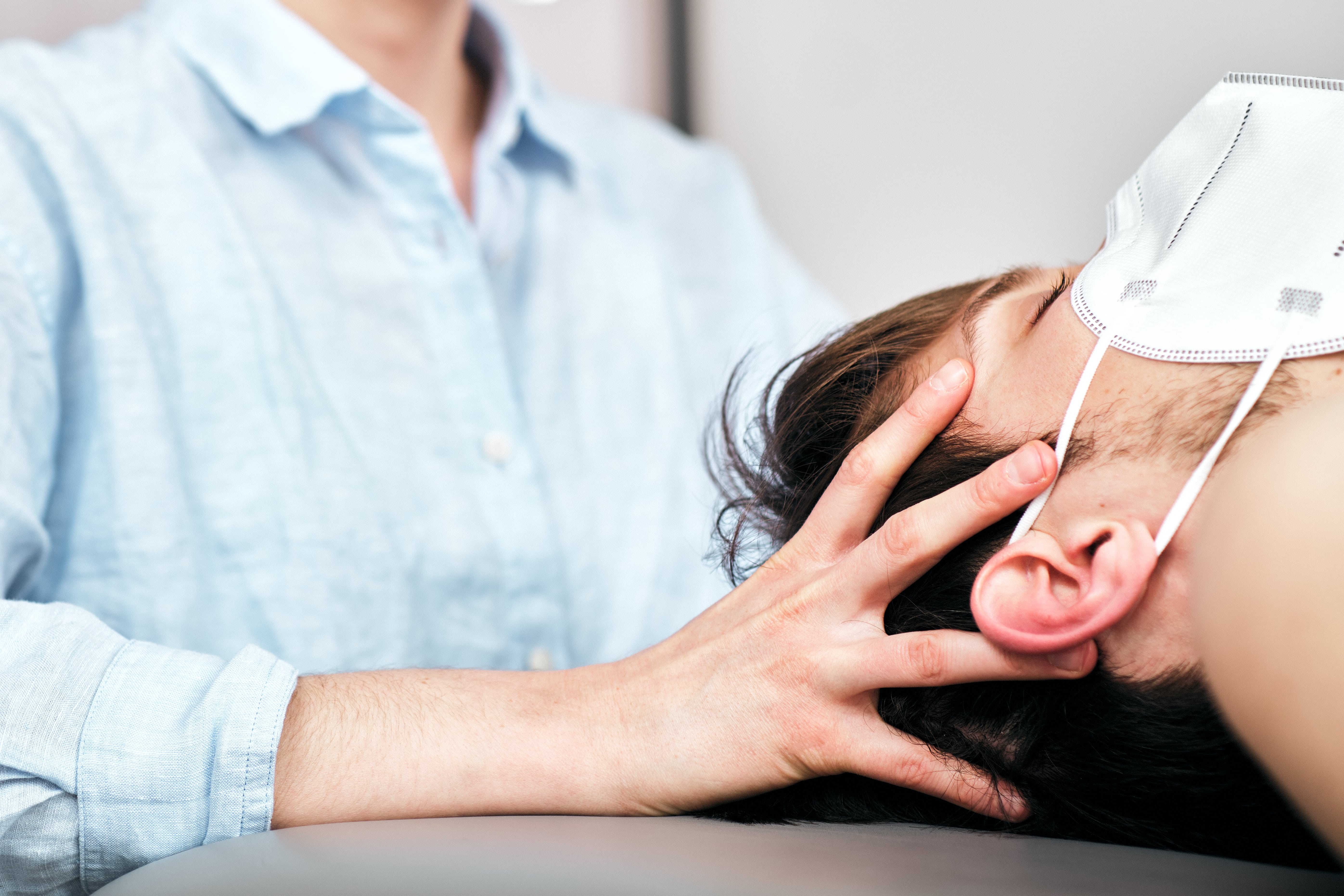
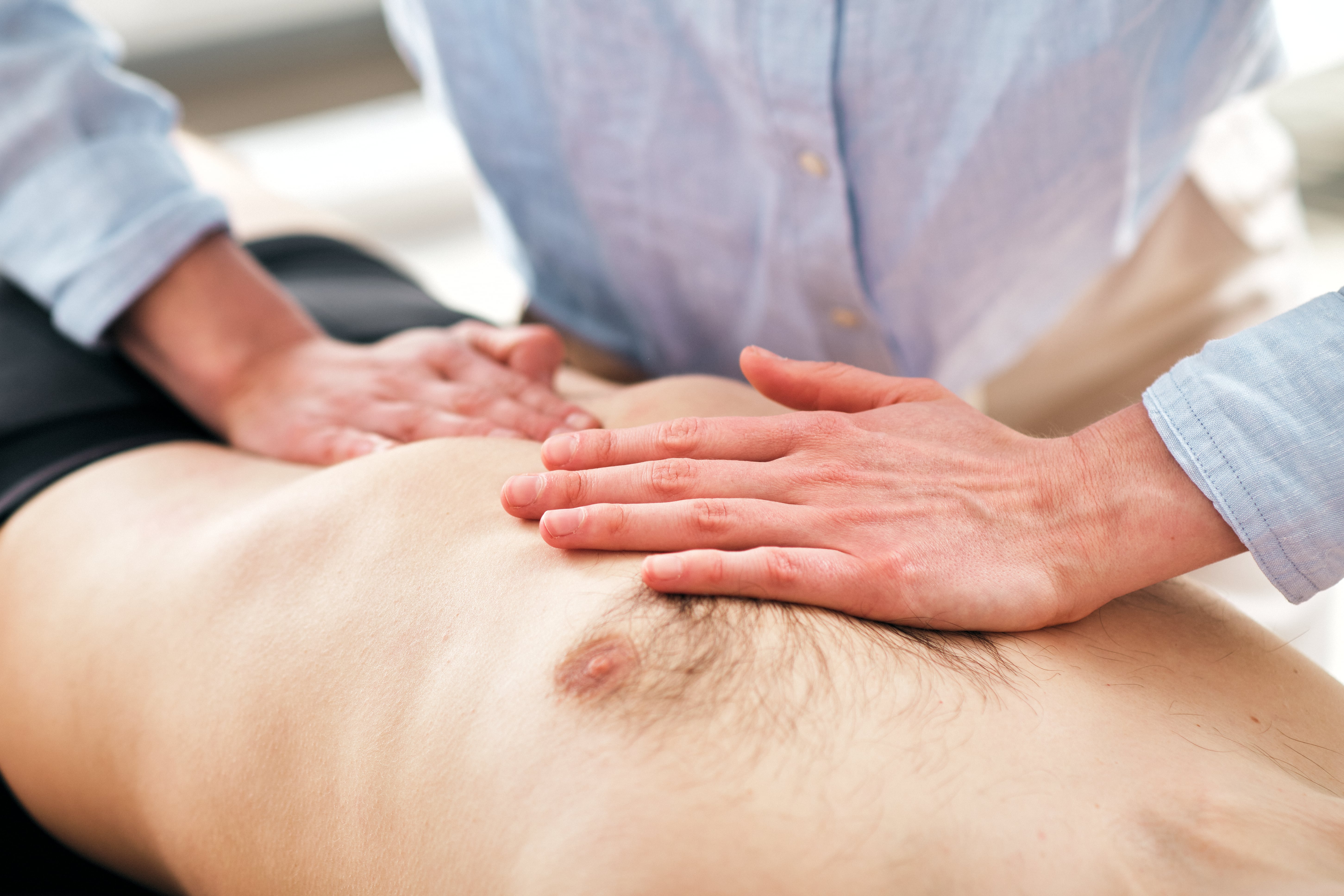
The osteopathic approach to health concerns is very important to me. Osteopathy is a manual therapy that restores balance and function in the body by relieving blockages and tension.
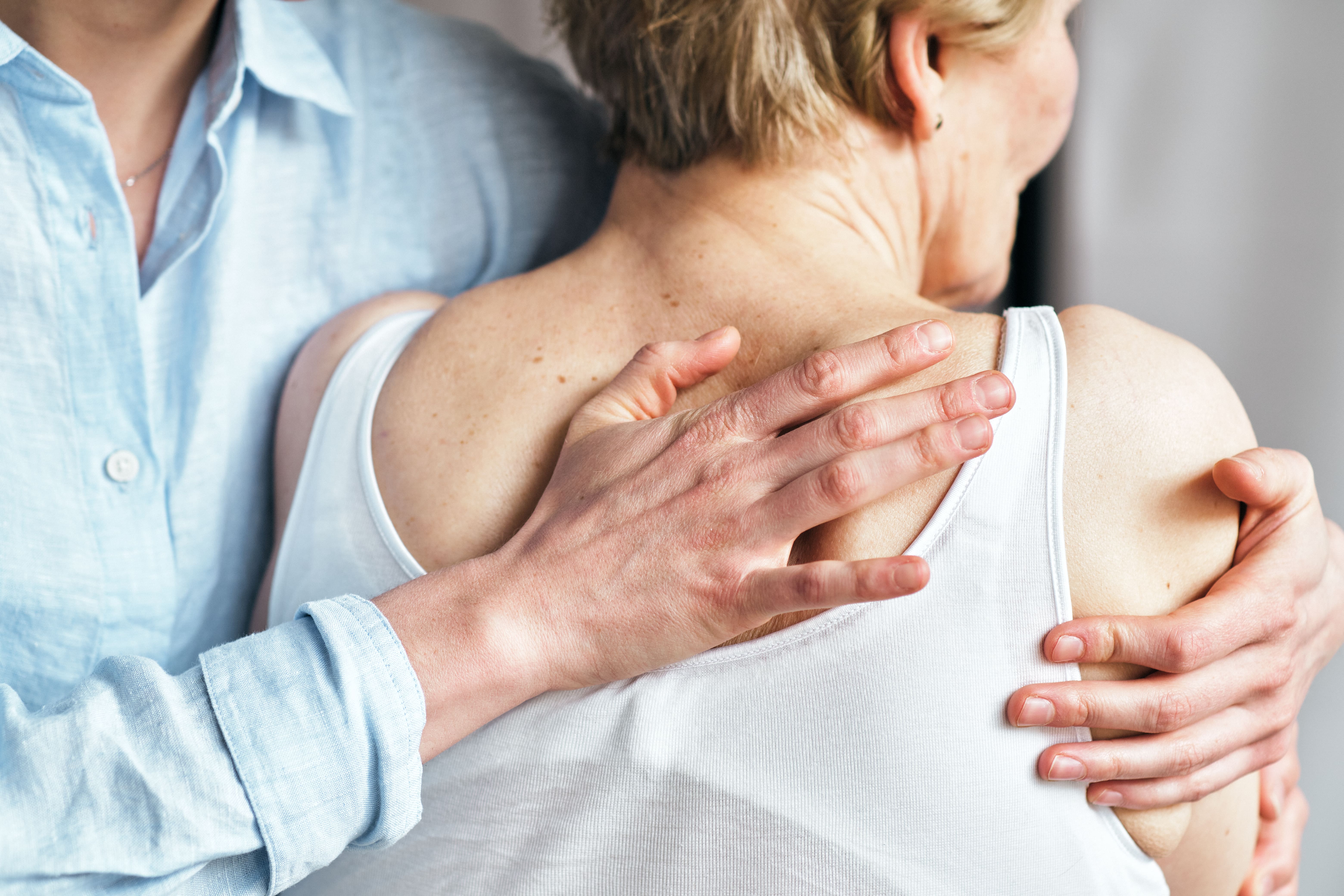
With my comprehensive training in classical osteopathy and pediatric osteopathy, I care for patients of all ages. I work in osteopathic diagnosis and treatment of traumatic birth consequences, developmental issues in infants, and functional restrictions across various systems in children and adolescents. Additionally, I cover the general applications of classical osteopathy for adults.
My practice specializes in osteopathic treatment for infants, children, and adolescents. Adults with physical complaints such as functional limitations, chronic or acute pain are also warmly welcome.
After a thorough case history and examination, I will provide suitable treatment recommendations for you or your child and develop an individualized therapy plan for you and your family to alleviate or counteract symptoms and discomfort. I actively advocate for the principle of patient self-efficacy in each individual’s health, and I am happy to inform you about potential causes of illness, symptom development, and the functioning of the human body.
On my website, you will find more information about the practice of osteopathy, the treatment process, costs, and appointment scheduling.
Yours sincerely, Maren Kammhoff (M.Sc. Osteopathy, HP)